
Overview
Teaching: 10 min
Exercises: 15 minQuestionsObjectives
- How can I share research code and data?
- Discuss the pros and cons of open science
- Learn how to mint a DOI for your project
Sharing research data
The Open Science movement encourages researchers to share research output beyond the contents of a published academic article (and possibly supplementary information).
Arguments in favor (from Wikipedia):
- Open access publication of research reports and data allows for rigorous peer-review
- Science is publicly funded so all results of the research should be publicly available
- Open Science will make science more reproducible and transparent
- Open Science has more impact
- Open Science will help answer uniquely complex questions
Arguments against (from Wikipedia):
- Too much unsorted information overwhelms scientists
- Potential misuse
- The public will misunderstand science data
- Increasing the scale of science will make verification of any discovery more difficult
- Low-quality science
(This image was created by Scriberia for The Turing Way community and is used under a CC-BY licence. The image was obtained from https://zenodo.org/record/3332808.)
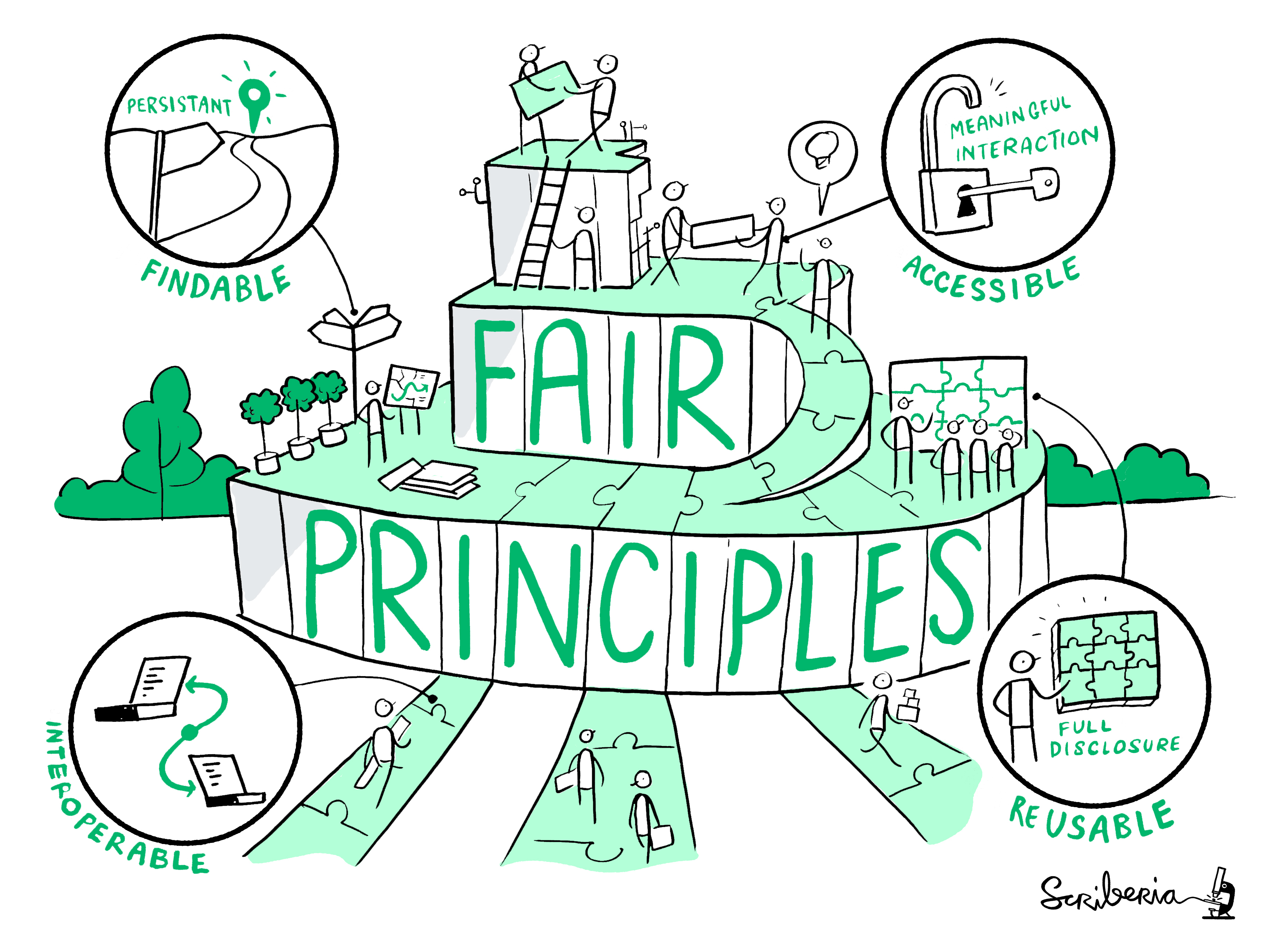
FAIR principles
(This image was created by Scriberia for The Turing Way community and is used under a CC-BY licence. The image was obtained from https://zenodo.org/record/3332808.)
“FAIR” is the current buzzword for data management. You may be asked about it in, for example, making data management plans for grants:
- Findable
- Will anyone else know that your data exists?
- Solutions: put it in a standard repository, or at least a description of the data. Get a digital object identifier (DOI).
- Accessible
- Once someone knows that the data exists, can they get it?
- Usually solved by being in a repository, but for non-open data, may require more procedures.
- Interoperable
- Is your data in a format that can be used by others, like csv instead of PDF?
- Or better than csv. Example: 5-star open data
- Reusable
- Is there a license allowing others to re-use?
Even though this is usually referred to as “open data”, it means considering and making good decisions, even if non-open.
FAIR principles are usually discussed in the context of data, but they apply also for research software.
Note that FAIR principles do not require data/software to be open.
Discussion: Discuss open science
- Do you share any other research outputs besides published articles and possibly source code?
- Discuss pros and cons of sharing research data.
Exercise: Get a DOI by connecting your repository to Zenodo
Digital object identifiers (DOI) are the backbone of the academic reference and metrics system. In this exercise we will see how to make a GitHub repository citable by archiving it on the Zenodo archiving service. Zenodo is a general-purpose open access repository created by OpenAIRE and CERN.
- Sign in to Zenodo using your GitHub account. For this exercise, use the sandbox service: https://sandbox.zenodo.org/login/. This is a test version of the real Zenodo platform.
- Go to https://sandbox.zenodo.org/account/settings/github/.
- Find the repository you wish to publish (e.g. the
word-countproject that you imported or another test repo), and flip the switch to ON.- Go to GitHub and create a release by clicking the
releasetab andCreate a new release(a release is based on a Git tag, but is a higher-level GitHub feature),- Creating a new release will trigger Zenodo into archiving your repository, and a DOI badge will be displayed next to your repository after a minute or two. You can include it in your GitHub README file: click the DOI badge and copy the relevant format (Markdown, RST, HTML).
Services for sharing and collaborating on research data
To find a research data repository for your data, you can search on the Registry of Research Data Repositories (re3data) platform and filter by country, content type, discipline, etc.
International:
- Zenodo: A general-purpose open access repository created by OpenAIRE and CERN. Integration with GitHub, allows researchers to upload files up to 50 GB.
- Figshare: Online digital repository where researchers can preserve and share their research outputs (figures, datasets, images and videos). Users can make all of their research outputs available in a citable, shareable and discoverable manner.
- EUDAT: European platform for researchers and practitioners from any research discipline to preserve, find, access, and process data in a trusted environment.
- Dryad: A general-purpose home for a wide diversity of datatypes, governed by a nonprofit membership organization. A curated resource that makes the data underlying scientific publications discoverable, freely reusable, and citable.
- The Open Science Framework: Gives free accounts for collaboration around files and other research artifacts. Each account can have up to 5 GB of files without any problem, and it remains private until you make it public.
Sweden:
Norway:
- NIRD archive is widely used by some communities
- NSD - Norwegian Center for Research Data, for any kind of data
- TSD - Norwegian Service for Sensitive Data
- Dataverse.no - Dataverse network, based at University of Tromsø but open for other institutions
Denmark:
Finland:
Further reading on reproducibility and open science
- The Turing way
- Illustrations from the Turing Way book dashes
- Reproduciblity syllabus
- The reproducible research data analysis platform
- Good talks on open reproducible research can be found here.
- “FAIR is not fair enough”
- “A FAIRer future”
- “Top 10 FAIR Data & Software Things” are brief guides that can be used by the research community to understand how they can make their research (data and software) more FAIR.
Key Points
Consider sharing other research outputs than articles.